Electromagnetic compatibility can be defined as any type of effect that does not produce electromagnetic interference in the case of the generation, transmission, and reception of electromagnetic energy. As a result of the standard, electromagnetic compatibility has become a very important criterion for the marketing of electronic products.
EMC consists of two major items: EMI(interference) and EMS(susceptibility).
RE (radiated, emitted), CE (conducted interference), Harmonic (harmonic), Flicker (flickering)
ESD (Electrostatic), EFT (Transient Pulse Interference), DIP (Voltage Dip), CS (Conducted Immunity), RS (radiation immunity), Surge (surge, lightning strike), PMS (power frequency magnetic field immunity)
As mentioned above, EMC includes two major test items: EMI and EMS. The key point of EMI verification is the amount of electromagnetic energy radiated by the electrical appliance itself during operation. The greater the energy, the greater the possibility of interfering with other electrical appliances.
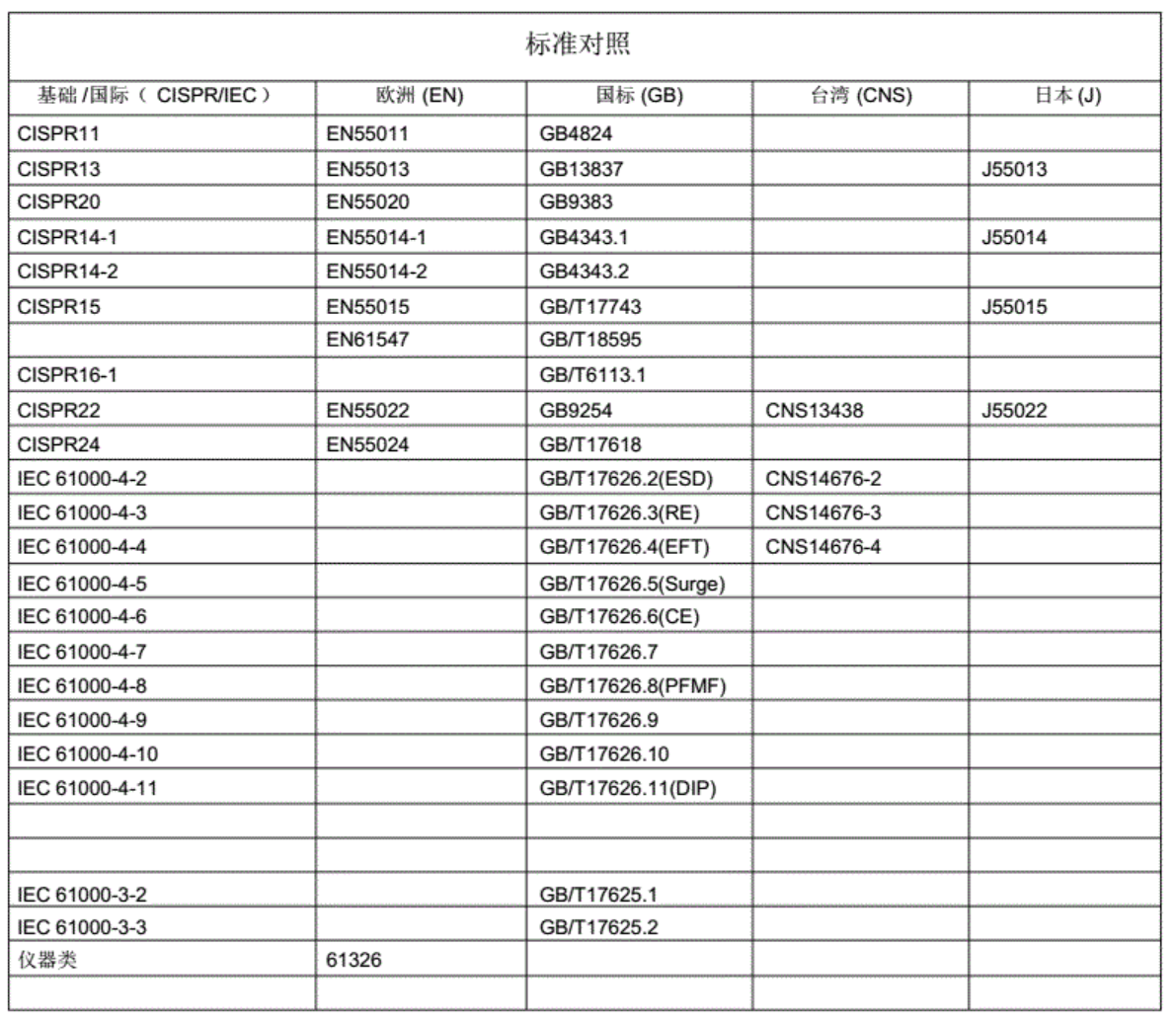
EMC standards define terms, rules, test methods, emission limits and immunity levels for Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC).
EMC standards Limited refe rence: